DOX Tools
October 19, 2019
The design of experiments (DOE, DOX, or experimental design) is the design of any task that aims to describe or explain the variation of information under conditions that are hypothesized to reflect the variation[1]. Montgomery specifies [2] experimental design is a tool for engineers and scientists to use for product design and development as well as process development and improvement.
Statistical software are specialized computer programs for analysis in statistics. In general, a statistical software is needed to calculate necessary numerical values when you analyze the subject in DOX. There are various statistical software tools[3] you can use in your study. Some authors prefer to use open-source, public domain, or freeware tools in their DOX books while others use proprietary software or add-ons.
Recommendations
z
An R Example
Example[2]
An engineer is studying the formulation of a Portland cement mortar. He has added a polymer latex emulsion during mixing to determine if this impacts the curing time and tension bond strength of the mortar. The experimenter prepared 10 samples of the original formulation and 10 samples of the modified formulation. We will refer to the two different formulations as two treatments or as two levels of the factor formulations. When the cure process was completed, the experimenter did find a very large reduction in the cure time for the modified mortar formulation. Then he began to address the tension bond strength of the mortar. If the new mortar formulation has an adverse effect on bond strength, this could impact its usefulness.
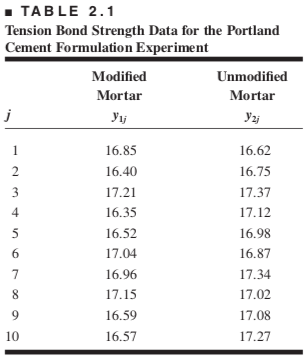
Figure: Screenshot of the Table 2.1. in Montgomery's book[2], p.26.
> t.test(y1,y2,var.equal=TRUE) Two Sample t-test data: y1 and y2 t = -2.1869, df = 18, p-value = 0.0422 alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to 0 95 percent confidence interval: -0.54507339 -0.01092661 sample estimates: mean of x mean of y 16.764 17.042
> t.test(y1,y2) Welch Two Sample t-test data: y1 and y2 t = -2.1869, df = 17.025, p-value = 0.043 alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to 0 95 percent confidence interval: -0.546174139 -0.009825861 sample estimates: mean of x mean of y 16.764 17.042
References
- ↑ Wikipedia. 2019. WikipediA: the Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Design_of_experiments.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Douglas C. Montgomery. 2013. Design and Analysis of Experiments (8th. ed.). Wiley, New York, NY.
- ↑ Wikipedia. 2019. WikipediA: the Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_statistical_software.